Projects
More Projects- Designed a synthesizable shallow Res-CNN for CIFAR-10, Pareto-optimal among 8 CNNs for parameter memory, accuracy & FLOPs
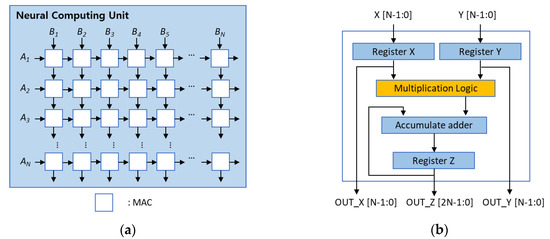
- Built systolic-array PEs with 8-bit CSA–MBE MACs, FSM-based control, 2-cycle ready/valid handshake, and verified TB operation
- Performed PTQ/QAT (Q1.31→Q1.3) analysis; Q1.7 PTQ retained ∼84% accuracy (<1% loss) with 4x smaller (∼52kB) memory footprint
- Auto-generated 14 coeff & 3 RGB ROMs via TCL/Py automation; validated TF/FP32–RTL consistency and automated inference execution
- Implemented AXI-Stream DIP toolkit (edge, denoise, filter, enhance) with pipelined RTL & FIFO backpressure handling
- MLP classifier on (E)MNIST (>75% acc.) with GUI viz; Automated preprocessing & inference with TCL/Perl
Verilog
SystemVerilog
TensorFlow
Python
TCL
Perl
AXI-Stream
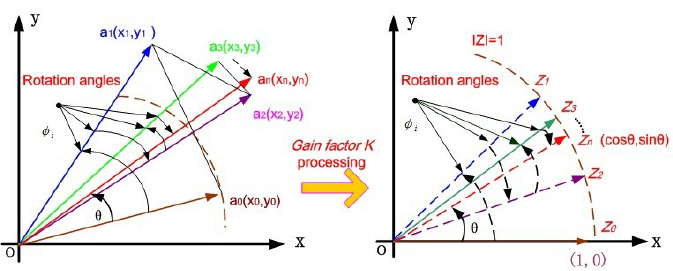
- Implemented shift-add datapath with all 6 modes rotation/vectoring (circular/linear/hyperbolic); width/iter/angle frac/output width–shift scaling swept across configs
- Built trig/mag/atan2/mul/div/exp wrappers; observed ∼e-5 RMS (@32b, 16iter) baseline vs double-precision references
- Proved handshake, deadlock-free bounded liveness, range safety, symmetry & monotonicity via SystemVerilog assertions (SymbiYosys/Yices2)
- Auto-generated atan tables & param files via Python; FuseSoC-packaged core with documented sensitivity, error trends & failure regions
- Variants: pipelined/SIMD/multi-issue; Systems: radix-2 FFT/IFFT, QAM16 receiver (Costas carrier + Gardner timing recovery)
Verilog
SystemVerilog
SymbiYosys
Yices2
Python
FuseSoC
- Benchmarked six 8-bit signed adders-multipliers via identical RTL2GDS Sky130 flow to isolate arithmetic-level post-route PPA trade-offs
- 3-stage pipelined systolic MAC (CSA-MBE), achieving ↓66.3% delay; ↑3.1× area efficiency; ↓82.2% typical power vs naïve conv3 baseline
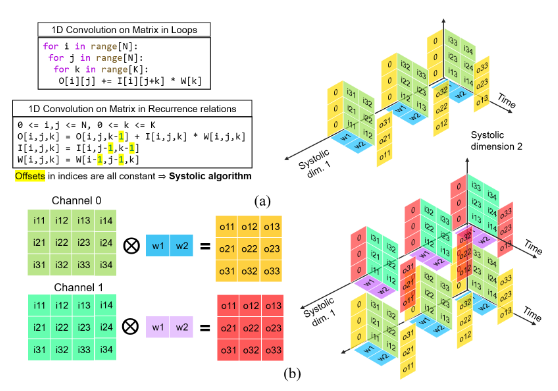
- Used a 2D PE-grid structure for convolution (verified 0/same padding modes) and optimized GEMM (reducing power by 44.6%; N = 3)
- Added a 648-bit scan chain across all pipeline/control registers, enabling full DFT/ATPG testability with only +14.5% cell overhead
Verilog
Sky130
RTL2GDS
OpenLane
DFT
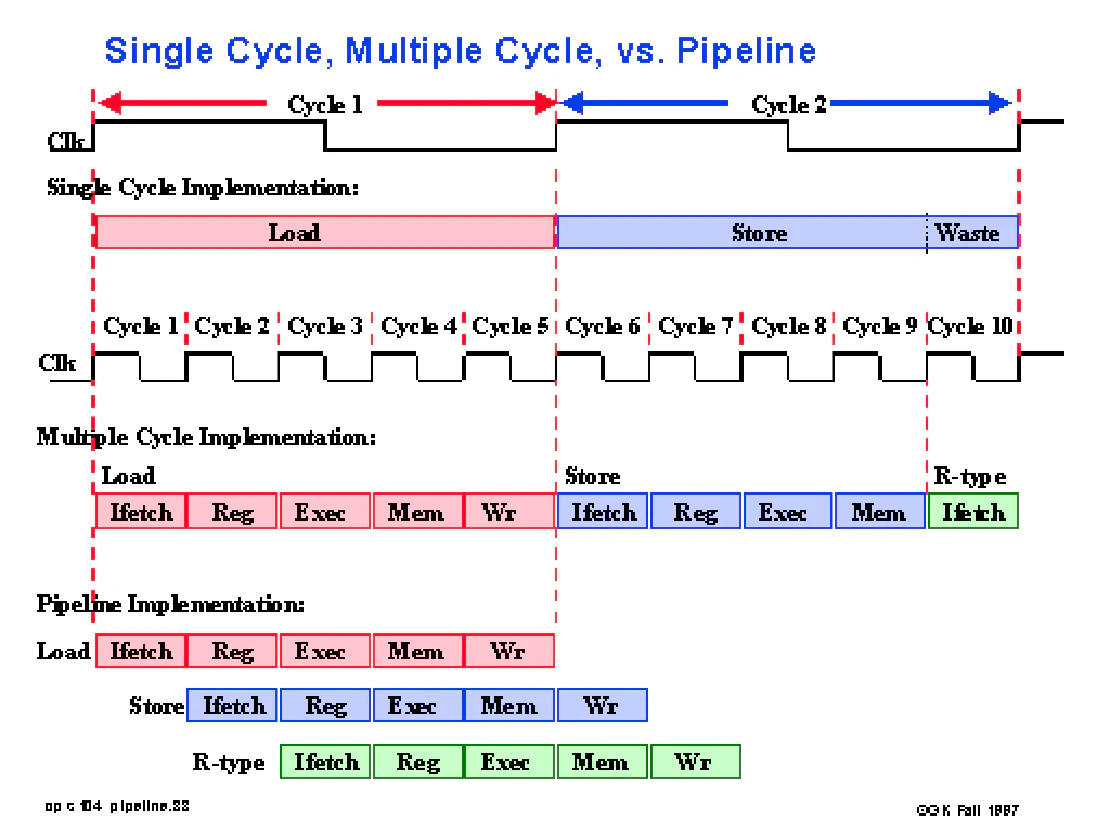
- Built a two-wide in-order superscalar RISC processor with parallel IF–ID–EX–MEM–WB lanes and independent pipeline registers per lane
- Designed dual 32-bit instruction fetch per cycle with inter-lane dependency checks, hazard suppression, and load-use stall handling
- Implemented 4R2W register file, RAW/WAW detection, branch squashing, & multi-port memory for concurrent fetch and data access
- Evaluated SC/MC/5-stage pipelined designs via directed programs (assembly with RISCV GCC Toolchain & QEMU reference), analyzing CPI (1/3.8/1.6), cycle counts, and hazard overhead
- Validated RV32I compliance using the RISC-V Architectural Compliance Test (RISCV-ACT), verified functionality with the Dhrystone benchmark
- Evaluated LUT utilization, CPI, and instruction throughput, achieving ~1.6 CPI and ~0.63 instructions/cycle throughput in the two-wide superscalar pipeline
Verilog
RISC-V GCC Toolchain
QEMU
- Designed non-pipelined/pipelined/scan-enabled 4-stage ALU; pipeline FFs replaced with scan FFs for scan-in/capture/scan-out; added CDC bridge (async FIFO + 2FF sync) between clk domains
- Gate-level timing analysis in Yosys/OpenSTA (Sky130) with clock uncertainty, I/O delays, & input slew; ∼1.7x fmax gain with pipelining
- RTL2GDS flow: scan vs no-scan, single vs dual scan, CTS skew tightening, util/density & floorplan stress; closed timing throughout
- Integrated scan-safe clock gating on pipeline regs; reduced switching power ~19% & internal power ~38% with negligible timing impact
- Analyzed IO-driven routing effects; worst-case pinning increased clock wire length by >2x despite CTS/placement optimization; recovered via pin-arch optimization (>50% clk WL ↓); PDN stress at signoff showed +21% total & +58% switching power
Verilog
Yosys
OpenSTA
Sky130
DFT
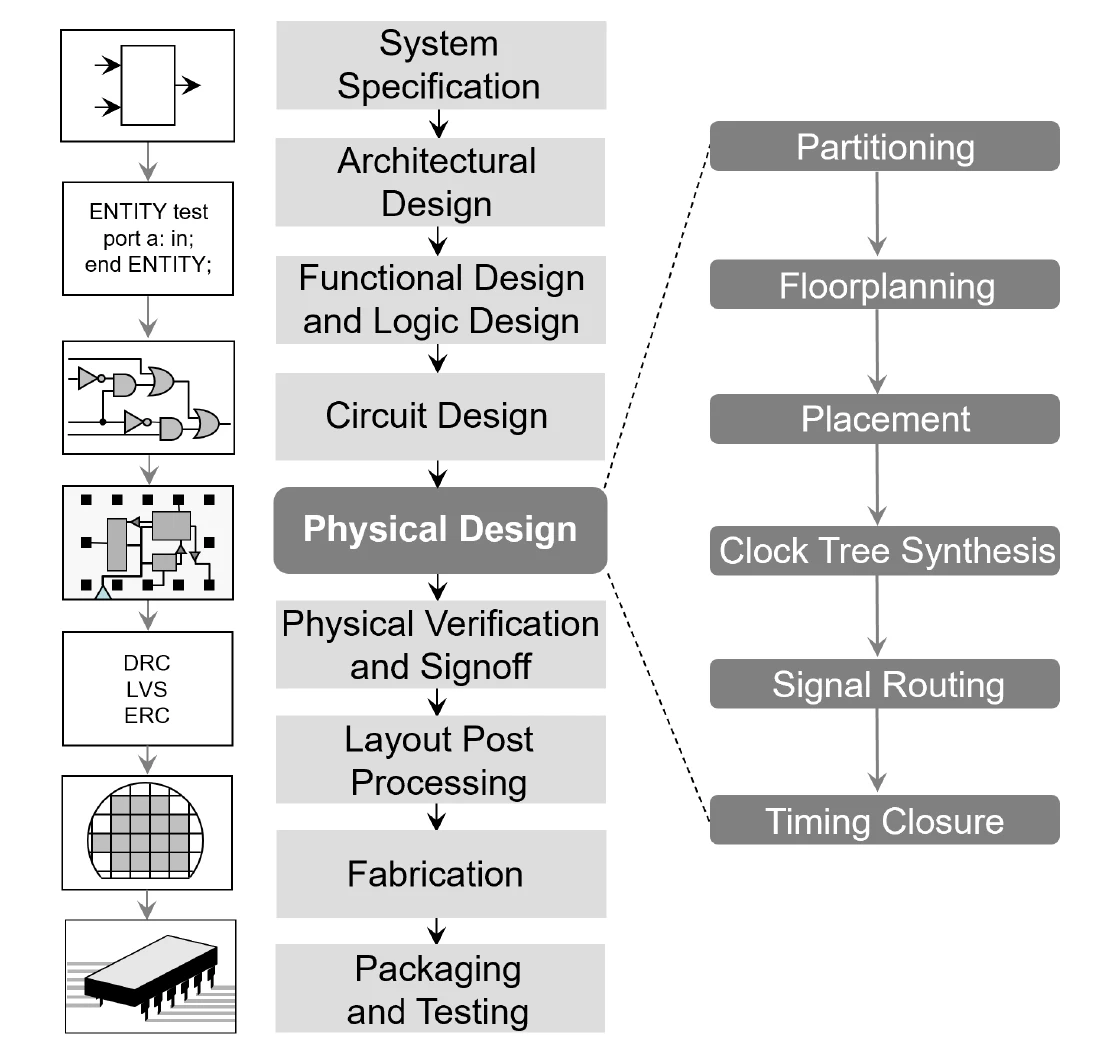
AHB–APB Bridge with Self-Checking Verification
- Designed a parameterizable AHB-Lite to APB bridge with FSM-based control supporting single & burst read/write transactions
- Implemented address/data latching, write buffering, read return, and burst sequencing, handling pipelined and non-pipelined accesses
- Built a self-checking SV testbench with macro-controlled test modes (single/burst R/W) and assertion-based data validation
- Verified protocol correctness across all transaction types; additionally designed & verified standalone (I2C/SPI/UART) peripheral controllers
Verilog
SystemVerilog
Functional & UVM Verification of SHA-256 Core (secworks)
- Developed a self-checking functional verification environment for the secworks SHA-256 core, validating compression rounds, IV initialization, message scheduling, and multi-block chaining
- Implemented directed, random, corner-case, and fail-case stimuli (e.g., `abc`, empty message, all-zero, all-ones) to verify digest correctness and interface handshake behavior (`ready`, `digest_valid`)
- Injected malformed control sequences, undefined inputs, and invalid block ordering to stress protocol robustness and confirm mismatch detection and failure reporting
- Automated compilation, simulation, and log aggregation through a TCL-driven regression flow, enabling repeatable runs and consolidated verification reporting
- Implemented a basic SystemVerilog/UVM verification environment with agent, driver, sequencer, monitor, and scoreboard to modularize stimulus generation and digest checking
Verilog
Icarus Verilog
TCL
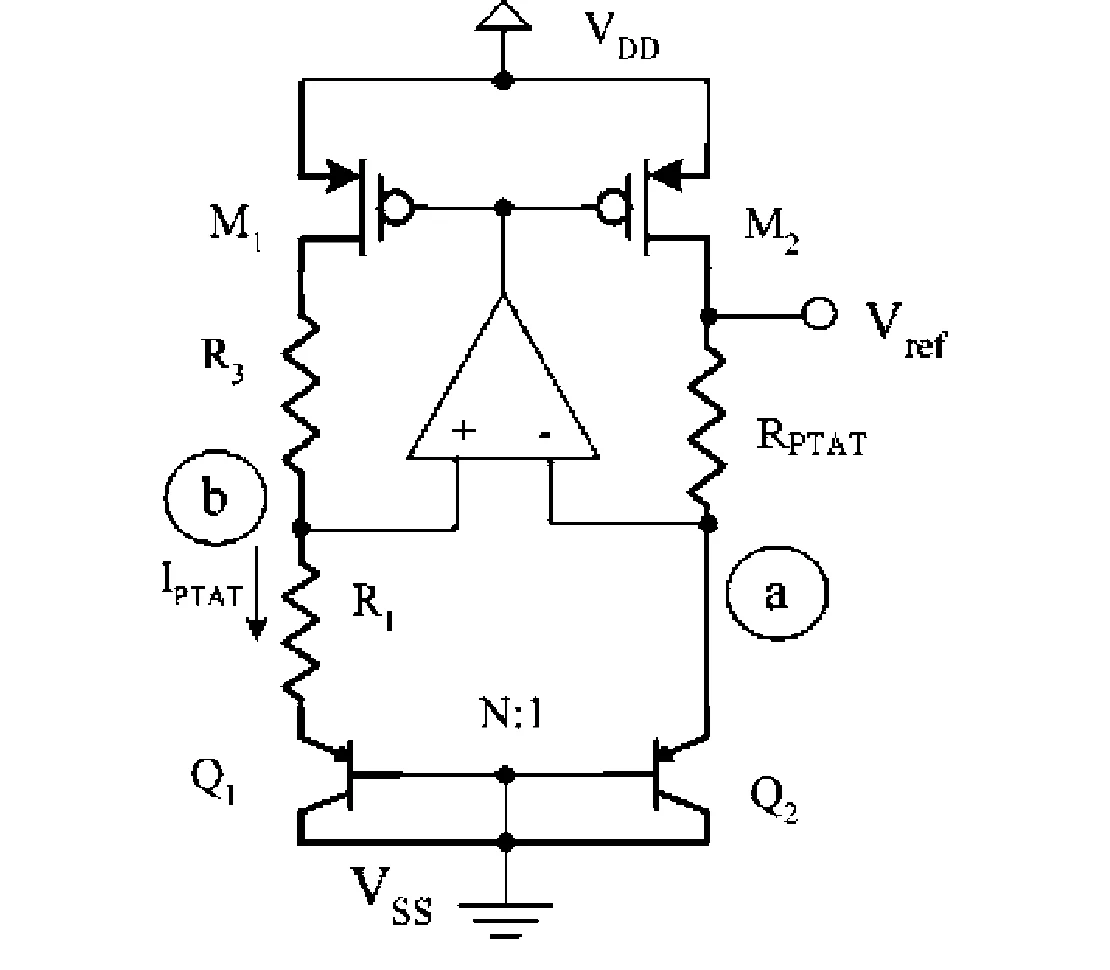
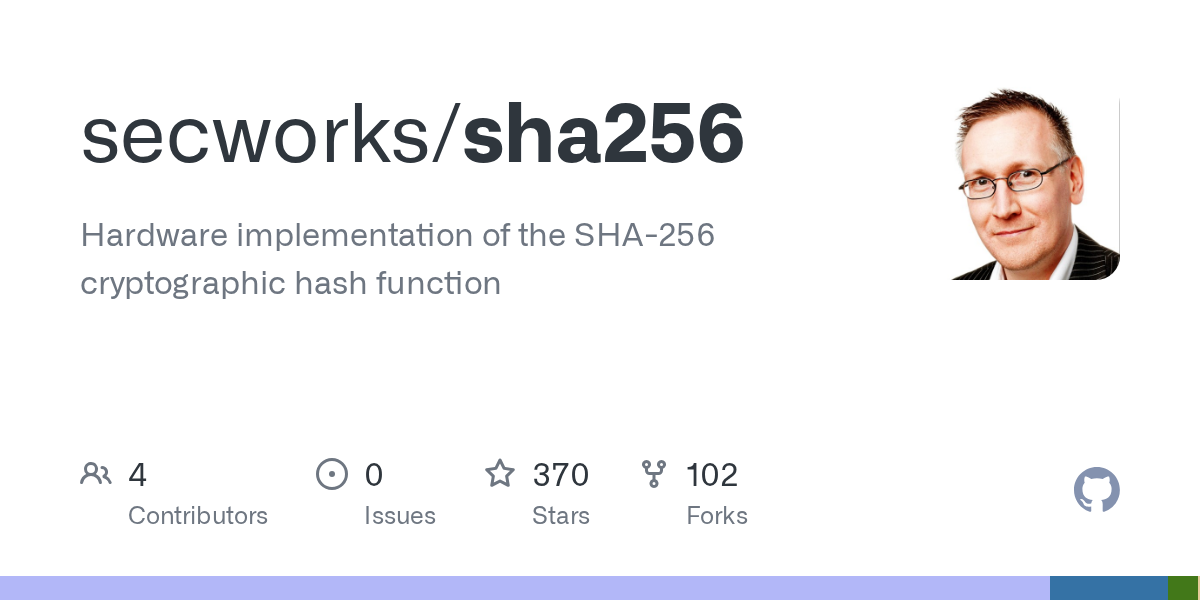
CMOS Bandgap Reference Simulation
- Simulated and verified a CMOS bandgap reference in OSU 180 nm CMOS using LTspice at a nominal 3.3 V supply
- Validated first-order temperature compensation by analyzing PTAT, CTAT, and Vref behavior across −40 °C to 200 °C
- Evaluated line regulation via DC supply sweeps from 2 V to 4 V and measured Vref sensitivity using waveform cursors
- Performed 100-run Monte Carlo mismatch analysis and quantified Vref variation with a standard deviation of 4.6 mV
LTspice
OSU 180nm CMOS
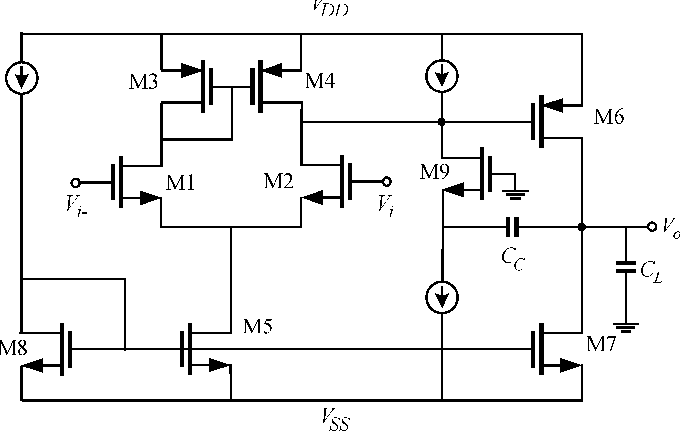
Two-Stage CMOS Op-Amp with Miller Compensation
- Designed an NMOS differential input pair with PMOS current-mirror load and common-source gain stage using Miller compensation, achieving 53.1 dB DC gain and 4.35 MHz unity-gain bandwidth
- Derived transistor sizing from slew-rate, input common-mode range, and gain constraints; verified correct biasing with a stable 0.60 V operating point
- Measured a 9.6 kHz −3 dB frequency, 448× small-signal gain, and clean 0.14–1.03 V output swing with no observable nonlinear distortion
- Evaluated key performance metrics including 1 mW power dissipation, 32 dB CMRR, 64.6/80.8 dB PSRR±, and 10 V/µs slew rate, confirming loop stability
LTspice
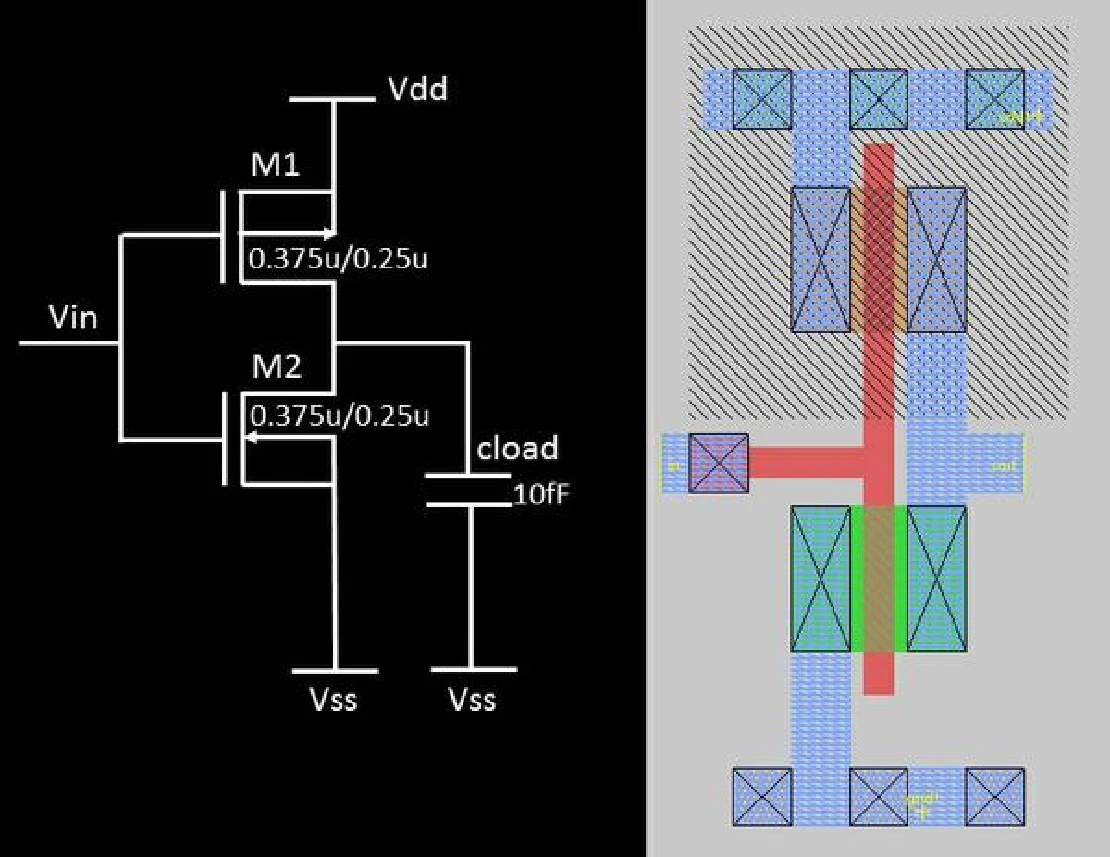
CMOS Inverter Layout & Post-Layout Simulation
- Built a CMOS inverter layout in Magic VLSI (SCMOS), including PMOS in n-well, NMOS in p-substrate, taps and contacts, and M1 routing; achieved DRC-clean layout
- Performed DC analysis in Ngspice on the extracted netlist to evaluate VTC behavior, observing VOH ~1.8 V, VOL ~0 V, and switching threshold VM ~0.95 V at 27 °C
- Analyzed transient switching behavior at 1.8 V operation, measuring TPHL ~282 ps, TPLH ~216 ps, and rise/fall times of ~0.50/0.53 ns
- Evaluated dynamic performance versus load conditions; observed average power ~2.51 µW and average current ~1.40 µA using Level-1 MOS models
Magic VLSI
Ngspice
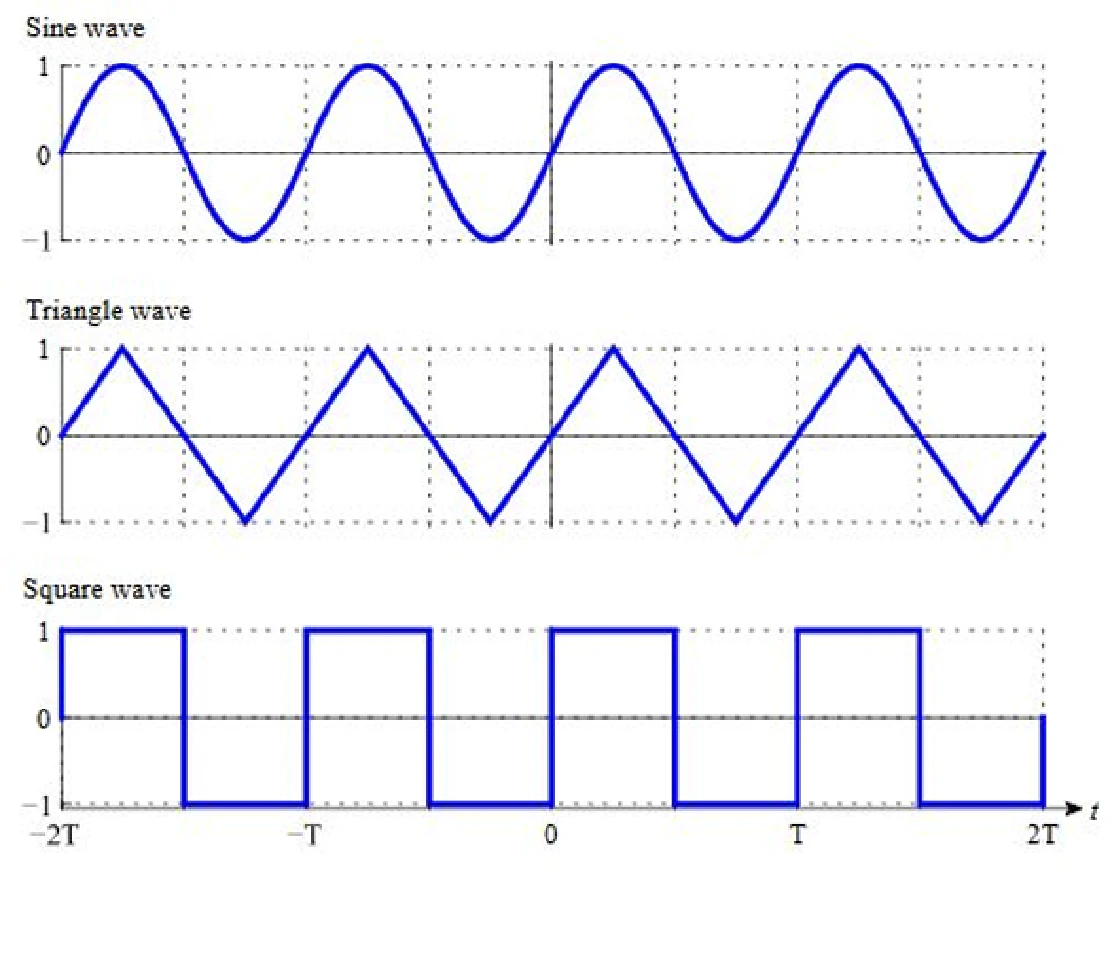
Analog Function Generator with Adjustable Amplitude, Offset, Phase, Modulation & VCO
- Designed an op-amp–based function generator using TL082, generating sine, square (<200 ns rise/fall), and triangular waveforms
- Implemented amplitude (±10 V), DC offset (±5 V), and phase control (0°–160°) over a 1 kHz–500 kHz operating range using a first-order all-pass filter
- Built the signal chain using a Wien-bridge oscillator, Schmitt trigger, integrator, and CD4051 multiplexer; validated via LTspice simulation and TI ASLK Pro hardware
- Integrated AM and PM modulation blocks along with a relaxation-oscillator-based VCO in LTspice, using unity-gain buffers to minimize inter-stage loading
LTspice
TL082
TI ASLK Pro
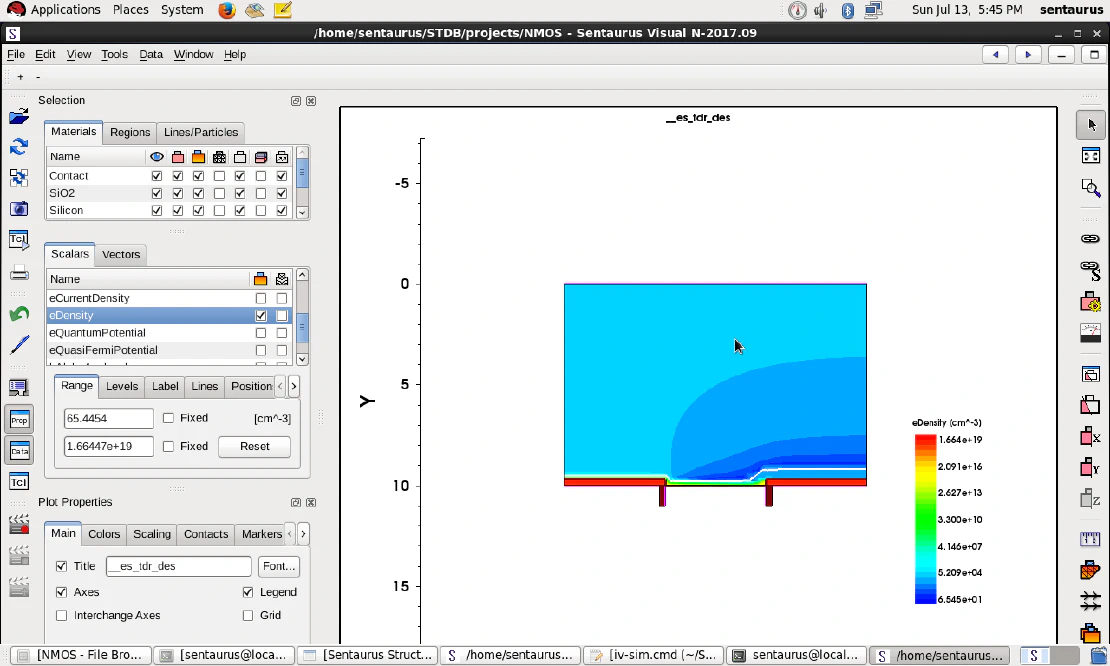
Semiconductor Device Modeling using Sentaurus TCAD
- Modeled N-resistor, PN diode, and NMOS devices in Sentaurus TCAD with parameterized doping profiles and device geometries
- Configured and automated process and device simulations using Sentaurus Workbench with command-based scripting workflows
- Analyzed and visualized electrostatic potential, carrier concentration distributions, and I–V characteristics using Sentaurus Visual and Inspect tools
Sentaurus TCAD
EDA Tools and ML-Based Design Analysis
- Python Tool for Analysis & Fault-Modeling (ISCAS’85/’89 Benchmark)
- Predictive ML-EDA Framework for Early Routability & Timing Sign-off (CircuitNet14)
- PCB Fault Classification and Detection (Akhatova/PCB-Defects | YOLOv7)
Python
Machine Learning
YOLOv7
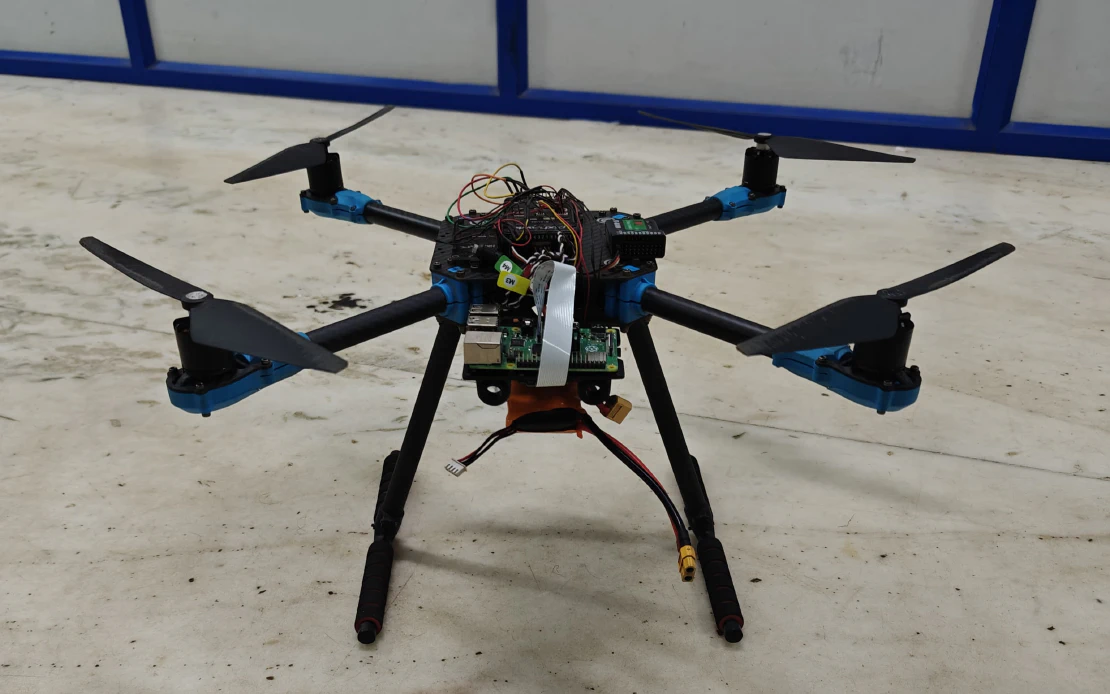
- Integrated NVIDIA Jetson Nano for onboard compute with Pixhawk 4 flight controller to enable autonomous navigation and precision landing
- Designed a sub-2 kg quadrotor optimized for GNSS-denied mapping, localization, and vision-based safe-zone detection
- Calibrated ESCs and implemented a stable 5 V / 3 A BEC power system; established bidirectional long-range telemetry using ESP32 (~500 m)
- Interfaced barometer, optical-flow, and stereo-vision sensors with Pixhawk over I2C and UART for fused state estimation
- Implemented visual–inertial odometry using ORB-SLAM3 and VINS-Fusion on ROS 2, achieving ~5 m localization with <5 cm drift
- Simulated Mars-like no-GPS flight scenarios in Webots with 0.38 g gravity, enabling autonomous landings within 1.5 m × 1.5 m safe zones
Jetson Nano
Pixhawk 4
ROS 2
ORB-SLAM3
VINS-Fusion
Webots
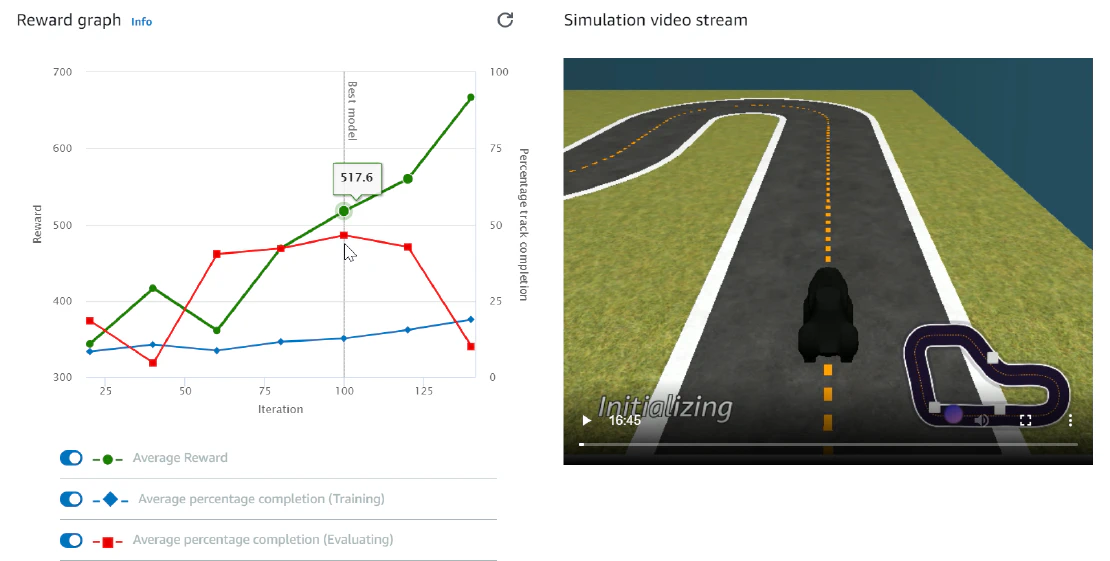
PPO-Based Reinforcement Learning for Autonomous Racing on AWS DeepRacer
- Trained continuous-action PPO agents on AWS SageMaker for end-to-end, camera-based autonomous racing with steering and speed control
- Designed reward functions emphasizing centerline stability, heading alignment, curvature-aware waypoint tracking, and velocity-weighted progress
- Stabilized training using distance-band shaping, steering smoothness constraints, and tuned PPO hyperparameters (entropy annealing, ε-clipping, GAE λ)
- Evaluated robustness under simulated perturbations including waypoint jitter, curvature sweeps, and speed-limit randomization
- Achieved consistent sub-2-minute lap times, outperforming default baselines and reaching top global leaderboard rankings in 2024
AWS SageMaker
PPO
Reinforcement Learning
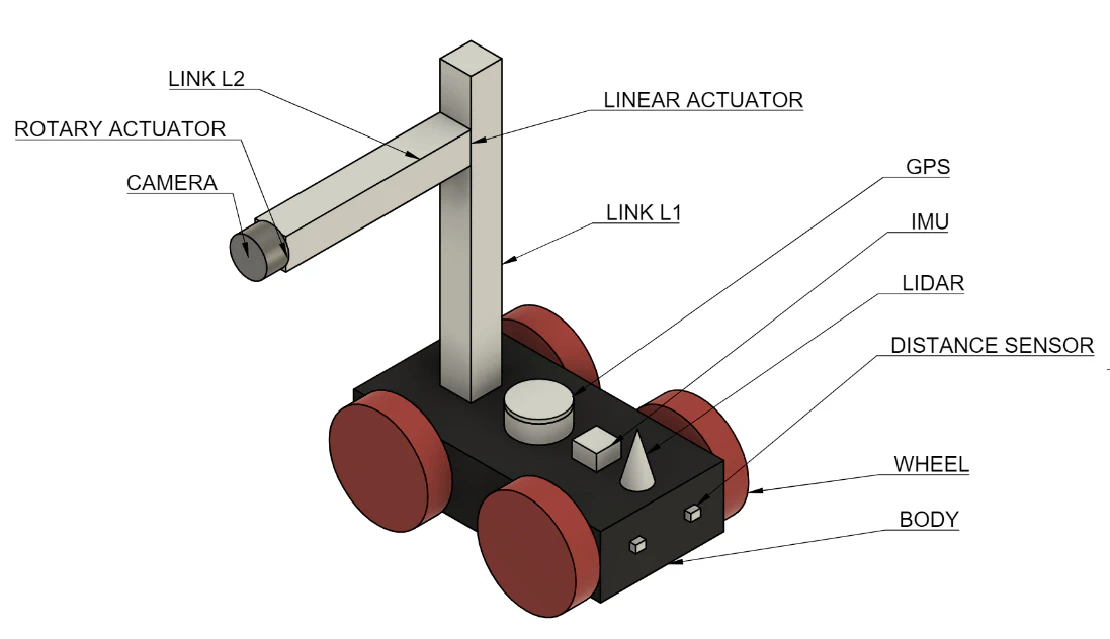
Autonomous Multi-Sensor Robot Simulation (GPS/IMU/LiDAR/2-DOF Vision)
- Developed a fully simulated 4-wheel autonomous robot equipped with GPS, 9-axis IMU, 2D LiDAR, ultrasonic distance sensors, and an actively actuated 2-DOF camera system
- Implemented global position tracking, local free-space detection, camera-based object observation, and reactive obstacle avoidance within the simulation stack
- Modeled sensor fusion inputs including GPS (x,y), IMU orientation/angular velocity, LiDAR ranging, and short-range distance sensing for collision-free navigation
- Designed independent wheel velocity control enabling smooth translation and turning, with teleoperation and autonomous wandering modes
- Built as a baseline multi-sensor robotics testbed for evaluating classical navigation and control behaviors without SLAM or learning-based methods
Simulation
Robotics
Sensor Fusion